Birth defects fall into three categories- structural, genetic, or chromosomal. Genetic or chromosomal abnormalities classify as developmental since they usually appear in the infancy stage. Structural congenital disabilities cause abnormalities in the structure of body parts. Some examples of birth defects include Congenital Heart Diseases, Clubfoot, Down Syndrome, Hypospadias, and Cleft Palate. Raising money for child surgery and treatments is usually difficult for underprivileged families in India.
Congenital Heart Diseases
Structural abnormalities such as Ventricular Septal Defect, or Atrioventricular Heart Defects, marked by holes in the heart valves are examples of congenital heart defects. Statistically, the occurrence rate for Congenital Heart Diseases is 9/1000 births. In India, there are over 200,000 such births annually. Depending on the specificity of the defect, symptoms may vary across the rapid heart and breathing rates, blue tinge to the lips or skin, or swelling of the legs, tummy, or around the eyes.
Concerning treatment, children who’s defects are detected in time, and receive the appropriate surgery and medication recover well and can live everyday lives. A children’s healthcare Foundation providing financial support for such children in India is Genesis Foundation. They can be reached at www.genesis-foundation.net.

Image courtesy: Medical Dialogues
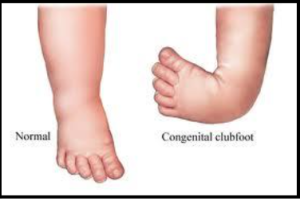
Clubfoot
Clubfoot is a structural birth defect marked by a twisted foot that is out of shape. Statistically, clubfoot has a global occurrence rate of 1 per 1000 live births, varying across different countries. A few weeks before the birth of the child, prenatal ultrasounds may detect the defect. Clubfoot’s most visually apparent symptoms are foot deformity, difficulty in walking, knock knees, or shortened legs. Despite the appearance, clubfoot is not painful or uncomfortable for children.
After detection and diagnosis, the optimal time for treatment is within the first month of the child’s birth. If left untreated, the discomfort for the child may increase. After treatment, usually through the Ponseti method, the child should be able to run and walk normally, provided that they receive treatment in time.
Down Syndrome
Down Syndrome is a genetic birth defect caused due to an irregular form of cell division. The syndrome includes many birth defects, denoted by a variety of symptoms. These include delayed development, reduced range of psychological capabilities, excess skin around the neck, mouth breathing, lazy eye, or speech problems, among many others. The occurrence rate is 1 per 800 live births.
Prenatal ultrasounds may reveal Down syndrome, but they cannot boast absolute accuracy. Concerning the treatment, there are treatment methods across self-care, therapies, or device intervention depending on the extent of the specific symptom being treated.

Haemophilia
Haemophilia is a genetic birth defect that adversely impacts the child’s blood clotting patterns. Symptoms include pain in the joints, blood in stool or urine, heavy or prolonged periods, internal bleeding, frequent nose bleeding, inexplicable bruises or swelling. The occurrence rate varies across the different types- Haemophilia A and Haemophilia B. The global incidence of Haemophilia A is 1 in every 5000 males and 1 in every 25,000 males for Haemophilia B.
Females can have haemophilia too, but the relative occurrence is almost negligible. Diagnosis for Haemophilia occurs through screening tests shortly after the child’s birth. Treatment spans medications and injections to improve blood clotting.
Cleft Palate
Cleft Palate is a genetic birth defect marked by a split in the opening of the mouth, caused in the womb due to an improper fusing of tissues. Symptomatically, the cleft palate may cause speech disorders, difficulties in feeding the baby, nasal congestion, impaired hearing and so on. Approximately 1 in 700 babies is born with a cleft palate defect.
While a few instances of the defect are diagnosed by prenatal ultrasounds, the rest become clear after the child’s birth, through physical examinations of the mouth and palate. Treatment of the defect spans different surgical interventions, including palatoplasty, or bone grafting. If necessary, the speech defects can be treated with speech therapy.
For families that cannot afford to raise money for child surgery, there are many children’s healthcare Foundations in India for financial support. Timely medical intervention is crucial in ensuring that children can live a quality life.
Read more: 6 Things without Which Website Maintenance is Incomplete


